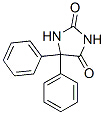
Phenytoin
| CAS No. | 57-41-0 | Cat. No. | BCP05960 |
| Name | Phenytoin | ||
| Synonyms | 5,5-Diphenylhydantoin;Lepitoin;Phenytek; Dilantin; | ||
| Formula | C15H12N2O2 | M. Wt | 252.27 |
| Description | Phenytoin is an antiepileptic drug. It is useful to treat partial seizures and generalized tonic-clonic seizures but not primary generalized seizures such as absence seizures or myoclonic seizures. Phenytoin is believed to protect against seizures by causing voltage-dependent block of voltage-gated sodium channels. Phenytoin has low affinity for resting sodium channels at hyperpolarized membrane potentials . When neurons are depolarized and the channels transition into the open and inactivated states, greater binding and block occur. The inhibitory potency is strongly use dependent, so that block accumulates with prolonged or repetitive activation, such as occurs during a seizure discharge. The blocking of sodium channels by phenytoin is of slow onset. The time course of fast sodium currents is therefore not altered in the presence of the drug and action potentials evoked by synaptic depolarizations of ordinary duration are not blocked. Thus phenytoin is able to selectively inhibit pat | ||
| Pathways | Ion Channel/Membrane Transporter | ||
| Targets | Sodium Channel | ||
Structure
Part data of this page collected from the open network resources, so Biochempartner can not guarantee its accuracy.
For product details of different batches, please contact our Customer
- Service & Tech Support:orders@biochempartner.com
- Website:www.biochempartner.com
Products are for research use only and not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
